What Is Blockchain? 4 Types Of Blockchain
Blockchain is a new type of digital record-keeping system. Think of it like a notebook where each page has a list of transactions. Once a page is full, it’s connected to the previous one, creating a chain of pages. This makes it really hard to change any old information, so everything stays secure and accurate. Blockchain was first used for digital money like Bitcoin, but now it’s used for many other things because it’s a trustworthy way to track and verify transactions.
There are four types of blockchain named as, Public Blockchains, Private Blockchains, Consortium Blockchains (Federated Blockchains), and Hybrid Blockchains. Let’s discuss the advantages and disadvantages of blockchain and their types.
What Is Blockchains?
A blockchain is a special kind of digital ledger or record book that keeps track of transactions securely and transparently. Imagine it like a chain of blocks, where each block is a group of transaction records. When a new block is added, it links to the previous block, forming a chain.
- Recording Transactions: When someone makes a transaction (like sending money), it’s recorded in a block.
- Adding to the Chain: This block is then linked to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks.
- Securing Information: Each block has a unique code called a hash, which makes it very hard to change once added. This keeps the information safe.
- Sharing the Ledger: All types of blockchain is shared with many computers, so everyone has the same record, making it hard for anyone to cheat.
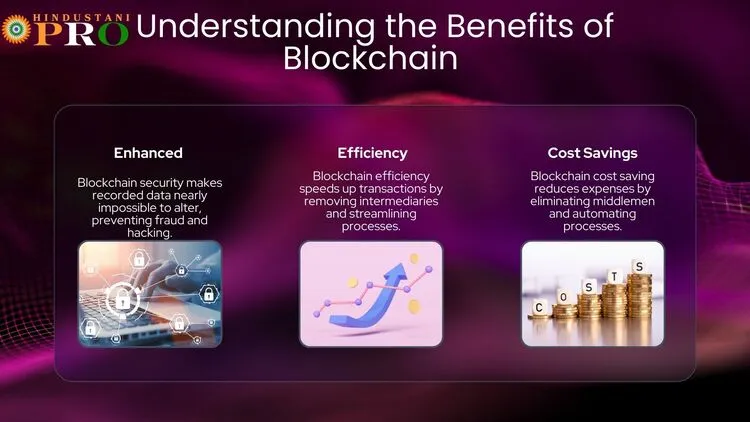
Advantages Different Types of Blockchain
Security
Blockchain is very secure because once information is added, it’s almost impossible to change or hack. Each block is linked and protected by a special code.
Transparency
Everyone can see the transactions on the blockchain, which makes it clear and honest. This helps prevent fraud and cheating.
Decentralization
Instead of having one central authority, like a bank, the blockchain is managed by many computers. This makes it more reliable and less likely to fail.
Efficiency
Transactions on a blockchain can be processed faster and without middlemen, like banks, which can save time and money.
Traceability
You can easily track and verify the history of transactions or assets, which is useful for things like supply chains and verifying product authenticity.
Disadvantages Different Types of Blockchain
Here are some disadvantages of four types of blockchain explained simply:
Slow Transactions:
Adding new information to the blockchain can be slow because every step needs to be verified by many computers. This can make transactions take longer.
High Costs:
Using and maintaining a blockchain can be expensive, especially because of the energy needed to run the network and the technology required.
Large Data Storage:
Types of Blockchain can grow very large as more information is added. This can require a lot of storage space and make it harder to manage.
Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is versatile and comes in various forms to suit different needs and levels of security. The four main types public, private, consortium, and hybrid each offer distinct advantages. Public blockchains are open and decentralized, making them ideal for transparency. Private blockchains provide controlled access for privacy within organizations.
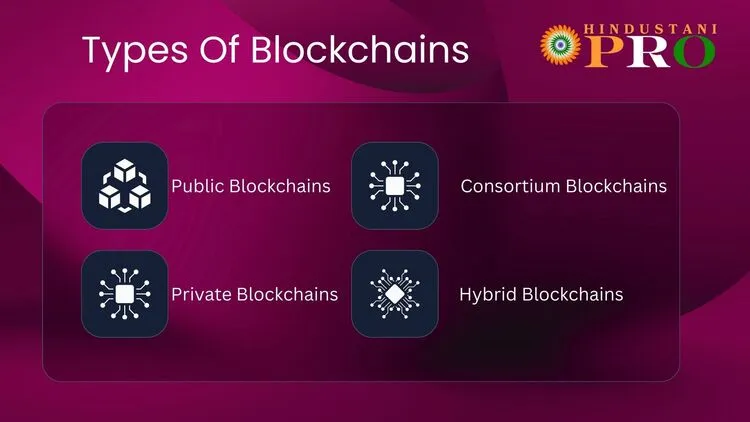
- Public Blockchains
- Private Blockchains
- Consortium Blockchains (Federated Blockchains)
- Hybrid Blockchains
Public Block Chains
A public blockchain is a digital record book that anyone can join and use. It’s like an open diary where everyone can see and check what’s written, making it fair and safe. No one person or company controls it, so it’s reliable and hard to cheat.
Pros and Cons Of Public Block Chains
| Pros: | Cons: |
| Open Access: Anyone can join and use the blockchain, making it very inclusive. | Slower Transactions: Transactions can take longer because they need to be verified by many participants. |
| Transparency: All transactions are visible to everyone, which helps ensure fairness and honesty. | Higher Costs: Operating and maintaining the blockchain can be expensive due to the energy and resources required. |
| High Security: The system is protected by many users, making it very difficult for anyone to cheat or hack. | Large Size: The blockchain can grow very large as it records every transaction, requiring significant storage space. |
| Decentralized: No single person or company controls the blockchain, so it’s more reliable and less likely to fail. | Decentralized: No single person or company controls the blockchain, so it’s more reliable and less likely to fail. |
Private Blockchains
A private blockchain is like a special, secret club where only certain people are allowed to join. Unlike a public blockchain, which anyone can join and see, a private blockchain is only for a specific group of people or companies.
Pros and Cons Of Private Blockchains
| Pros: | Cons: |
| Faster Transactions: Private blockchains can process transactions more quickly because they are managed by a smaller group of trusted participants. | Less Transparency: Since access is restricted, not everyone can see or verify the transactions, which can reduce transparency. |
| Lower Costs: Operating a private blockchain can be less expensive since it doesn’t require the same level of energy and resources as public blockchains. | Centralized Control: The blockchain is controlled by a single organization or a limited group, which can make it less decentralized and more susceptible to control or manipulation. |
| Controlled Access: Only authorized participants can access and use the blockchain, which enhances privacy and security within a trusted group. | Limited Participation: Fewer people are involved in maintaining the blockchain, which can affect its resilience and security compared to a public blockchain. |
| Customizable: Organizations can tailor the blockchain to fit their specific needs and requirements, making it more flexible. | Potential for Trust Issues: Participants need to trust the controlling entity or group, which might not be ideal for all applications, especially those requiring high levels of trust and independence. |
Consortium Blockchains (Federated Blockchains)
A consortium blockchain, or federated blockchain, is like a special group project where only a few trusted organizations are involved. Instead of everyone being able to join, only these selected members can access and manage the blockchain.
Pros And Cons Of Consortium Blockchains
| Pros: | Cons: |
| Faster Transactions: Consortium blockchains often have faster transaction speeds because a limited number of preapproved participants handle the verification process. | Limited Transparency: Transparency is lower compared to public blockchains because only consortium members can see and verify the transactions. |
| Lower Costs: Operating costs can be reduced compared to public blockchains because the infrastructure is shared among the consortium members, and less energy is used. | Centralized Control: Even though it’s decentralized among the consortium, control is still held by a limited number of participants, which can lead to trust issues or potential conflicts. |
| Controlled Access: Only selected organizations or entities can participate, which enhances privacy and control over who can access and modify the blockchain. | Complex Governance: Decision-making and governance can be complex due to the need for consensus among multiple parties, which can slow down changes or updates. |
| Collaboration: Multiple organizations can work together on a shared blockchain, allowing for cooperation and shared resources. | Potential for Bias: The participating organizations might have conflicts of interest or biases, affecting the fairness and neutrality of the blockchain. |
| Customizable: The blockchain can be tailored to the needs of the consortium members, allowing for more specific and relevant features and protocols. |
Looking for ways to boost your income? Check out our latest post on How to Make ₹50,000 a Month: 35+ Ways for some great ideas and tips to help you earn more every month!Hybrid blockchains
A hybrid blockchain is a type of blockchain that combines features of both public and private blockchains. It uses some aspects of public blockchains, like openness and transparency, while also incorporating elements of private blockchains, such as control and privacy.
Pros And Cons Of Hybrid Blockchains
| Pros: | Cons: |
| Balanced Privacy and Transparency: Hybrid blockchains allow you to control which information is shared publicly and which is kept private. This provides the best of both worlds, offering transparency where needed and privacy where required. | Complexity: Implementing and managing a hybrid blockchain can be complicated because it involves blending the characteristics of both public and private blockchains. |
| Customizable: They can be tailored to specific needs, combining features of both public and private blockchains to suit different use cases. | Partial Decentralization: Hybrid blockchains might not be as decentralized as purely public blockchains, potentially affecting their trustworthiness and resilience. |
| Enhanced Security: Sensitive information can be kept private while still allowing some data to be shared openly. This setup can enhance overall security and trust. | Higher Costs: Running a hybrid blockchain can be more expensive due to the need to manage and maintain both public and private components. |
| Efficient Performance: By integrating public and private features, hybrid blockchains can offer improved efficiency and faster transaction times compared to purely public systems. | Limited Adoption: Hybrid blockchains are less common and may not be as widely understood or supported as other types of blockchain. |
Explore our official website for more informative blog click here: Hindustani Pro
Bottom line
Hybrid blockchains are less common than public or private blockchains, so they might not be as widely understood or supported.
Types of Blockchains let you share some information with everyone while keeping other details just for a small group. Types of Blockchain makes them useful and flexible for many needs. However, they can be more complicated to set up and use, cost more to run, and aren’t as common as other types. So, they’re a great option when you need both privacy and openness in one system.